Molecular Bioprocessing Research
Chromatography
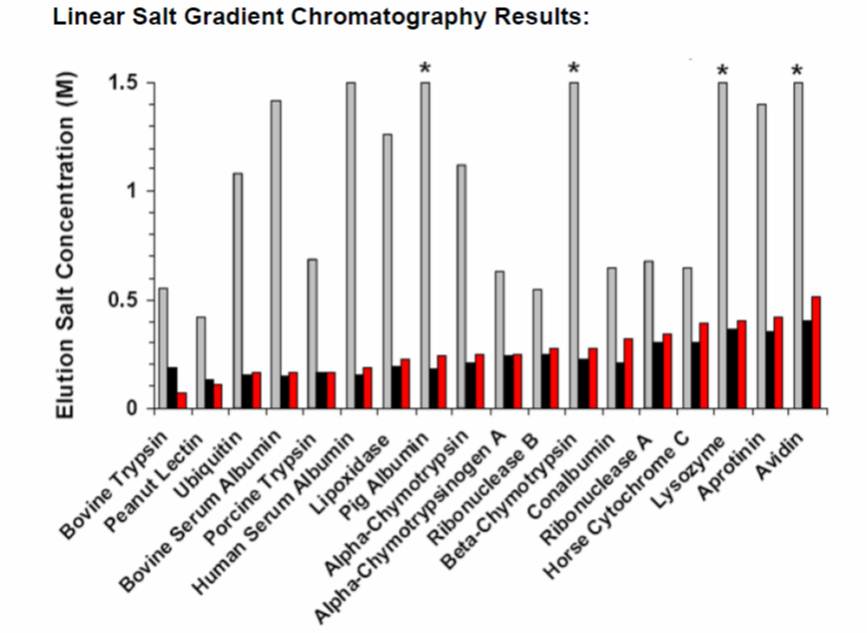
Batch and column chromatography experiments are used extensively in our laboratory to study protein-ligand interactions by generating adsorption isotherm parameters and protein retention models with a variety of chromatographic resins including ion exchange (IEX), hydrophobic interaction (HIC), hydroxyapatite, and multimodal (MM) resins. We employ both isocratic and gradient elution modes in our column chromatography studies in order to develop predictive models of protein retention behavior. Chromatographic studies have been carried out using diverse model protein libraries as well as homologous series. Current research efforts focus on understanding the interactions between antibodies and antibody-related proteins with multimodal ligands.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
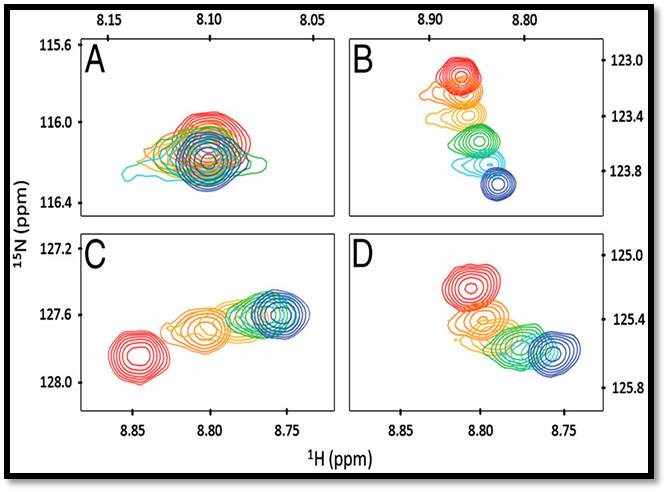
Nuclear magnetic resonance is widely employed for protein structure determination and protein-target interactions. In our studies, two-dimensional heteronuclear single quantum correlation experiments are employed to study the interactions of proteins with ion exchange and multimodal chromatographic ligands in solution. This technique makes it possible to identify the ligand interaction sites on a protein surface and the apparent binding affinities for each amino acid residue. Saturation transfer difference (STD) NMR experiments are routinely used for examining protein-ligand binding in solution and this technique is often used as an initial screening technique for evaluating the chemical moieties involved in binding.
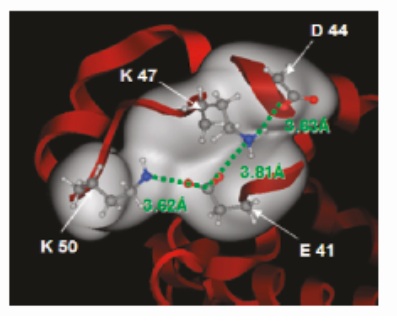
Molecular Simulations
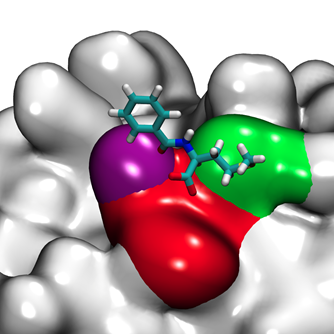
Over the course of the past decade, significant advances in simulation speed and accuracy have made computational molecular modeling a powerful tool for investigating complex intermolecular interactions. Our lab employs Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations to develop a fundamental understanding of protein-surface interactions in chromatographic systems. In particular, we are interested in investigating how different ligand chemistries and densities result in different protein-ligand interactions, which ultimately lead to differences in selectivity for different proteins.
Column Modeling
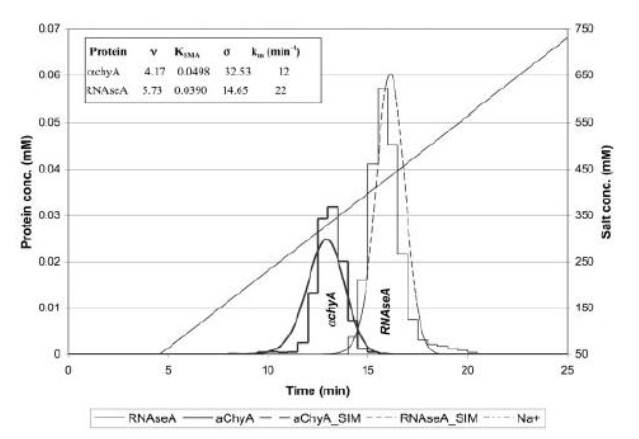
Column modeling has been a major area of research of the Cramer group. We have worked on modeling ion exchange, displacement, immobilized metal affinity and hydrophobic interaction chromatography. The ability to effectively model chromatographic profiles can give many insights into the fundamentals and mechanisms of the chromatographic process as well as being used as a powerful predictive tool. It can also help to explore experimental conditions much faster than experimental methods without the need for large quantities of materials mechanisms of the particular process.
Quantitative Structure Activity Relationship (QSAR) Models
QSAR is a powerful analytical method used in our lab to predict protein behavior based on a numerical description of surface properties, such as charge and hydrophobicity. Machine learning techniques are used to develop empirical correlations that can not only predict protein behavior but also provide insight into important interactions in chromatography systems. Current areas of research include applying the QSAR approach to model protein behavior such as viscosity and aggregation as well as the development of new classes of ligand and protein descriptors.

Smart Biopolymer Affinity Precipitation Systems (with Wilfred Chen, UDel)
Development of an ELP based smart biopolymer fusion protein affinity precipitation systems for purification of antibodies and new classes of biopharmaceuticals. Our aim is to determine the robustness and scalability of these purification systems. We employ robotic HTS techniques to investigate the effect of a variety of operating conditions on antibody yield, purity and quality at various stages of the process. Additionally, various microscopy techniques are used to characterize the PSDs of the precipitates.
Other techniques
We have employed several other techniques, including Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM), Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC) and Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR), to study the thermodynamics and kinetics of protein interactions with chromtographic ligands under various conditions.